Background
HLA-G (Human Leukocyte Antigen-G) and LILR (Leukocyte Immunoglobulin-Like Receptors) proteins are pivotal in the regulation of immune responses, playing crucial roles in maintaining immune tolerance and preventing overactive immune reactions. HLA-G is primarily known for its immunosuppressive properties, particularly in maternal-fetal tolerance during pregnancy, while LILR proteins are integral in modulating immune cell signaling. Together, they form a sophisticated network of interactions that balance immune activation and inhibition, making them essential targets in therapeutic research for autoimmune diseases, transplant acceptance, and cancer immunotherapy. At KACTUS, we offer a comprehensive range of high-quality recombinant HLA-G and LILR proteins, designed to support cutting-edge research and development in immunology and therapeutic applications.
Product Features
Available Products
HLA-G Proteins
Available Products
LILRA, LILRB, and APOE Proteins
About HLA-G & LILRs
What is HLA-G?
MHC-I proteins present antigenic peptides and are recognized by associated receptors. This enables the immune system to detect self-antigens and eliminate targets lacking self-antigens or expressing foreign antigens. Human leukocyte antigen G (HLA-G) is a non-classical human MHC class Ib molecule. It is an important immune tolerance molecule in the body, contributing to immune escape or immune cell anergy. In recent years, it has been regarded as a new type of immune checkpoint.
HLA-G, like other immune checkpoints, mediates its function by binding to receptors on immune cells. The known receptors of HLA-G are leukocyte Ig-like receptor subfamily B member 1 (LILRB1) and member 2 (LILRB2) which belong to the Leukocyte Ig-like receptor (LILR) family. LILRs are one kind of these receptors that either activates (LILRA members) or suppresses (LILRB members) immune cell functions. When HLA-G binds to LILRBs, tumor cells can escape the surveillance of the immune system. As LILRBs have a similar immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) like immune checkpoint proteins such as CTLA4 and PD-1, they've become hot targets for drug development, especially for discovery of first-in-class drugs.
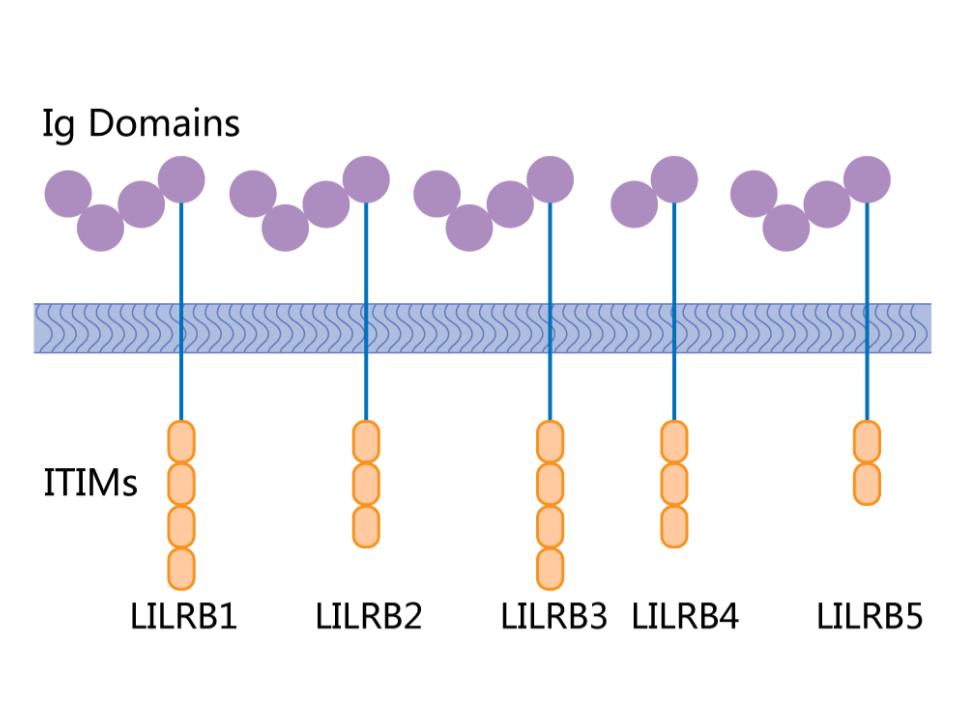
Figure 1. LILRB binding ligands.
What are LILRs?
Leukocyte Immunoglobulin-Like Receptors (LILRs) are a family of receptors primarily expressed on immune cells, playing critical roles in modulating immune responses. They are type I transmembrane glycoproteins characterized by the presence of extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains. LILRs can be activating (LILRAs) or inhibitory (LILRBs), with the inhibitory receptors possessing immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) in their cytoplasmic tails. These receptors recognize a variety of ligands, including major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules, and their interaction with these ligands can influence the function of various immune cells, including dendritic cells, macrophages, and T and B lymphocytes.
Novel Combination of Targets in Immune Response and Drug Discovery
Through these interactions, LILRs contribute to the regulation of both innate and adaptive immune responses, playing roles in immune tolerance, inflammation, and the defense against pathogens. Their dysregulation has also been implicated in various diseases, including autoimmune conditions, cancer, and infectious diseases. This highlighting their importance in immune homeostasis and their potential as therapeutic targets.
Moreover, multiple clinical/preclinical studies show the potential broad anti-tumor effects of LILR family proteins, such as BND-22 (Biond), IO-202 (Immune Onc), JTX-8064 (Jounce Therapeutics) and NC410 (NextCure). In addition, since the expression profile of HLA-G is significantly different from that of PD-L1, HLA-G antibodies might be able to enhance tumor sensitivity to anti-PD-L1 therapy. This would be a novel breakthrough for patients with tumors that do not respond to anti-PD-L1 therapy.