Membrane Protein Technology Platforms
Multipass transmembrane proteins play essential roles in cell growth, signal transduction, and intercellular communication, extensively involved in various physiological processes. They are also important targets for drug discovery and development. However, producing soluble recombinant forms of these proteins has long been a significant challenge, impeding the progress of new drug discovery.
We have developed two transmembrane protein display platforms: virus-like particles (VLPs) and nanodiscs, designed for robust, functional display of full-length, multipass- transmembrane proteins in their native conformation. Our platform technology preserves the structural integrity and biological activity of the membrane proteins, enabling a broad range of applications, including immunization, antibody screening, analytical assays such as SPR, BLI and ELISA. Our transmembrane protein products undergo strict bioactivity and purity testing using SPR, ELISA, flow cytometry, and HPLC, ensuring outstanding functional performance and high batch consistency for reproducible results.
Virus-like Particle (VLP)
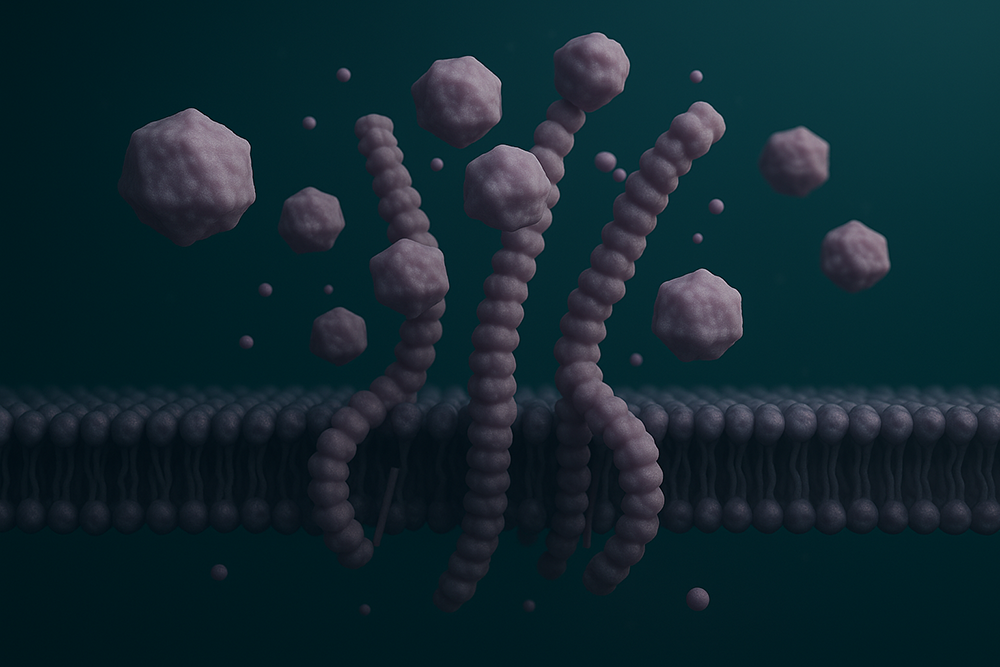
Virus-like particles (VLPs) are non-infectious nanoscale structures that closely mimic the organization and shape of native viruses but lack viral genetic material. They comprise self-assembled viral structural proteins and are highly immunogenic due to their repetitive, multivalent surface.
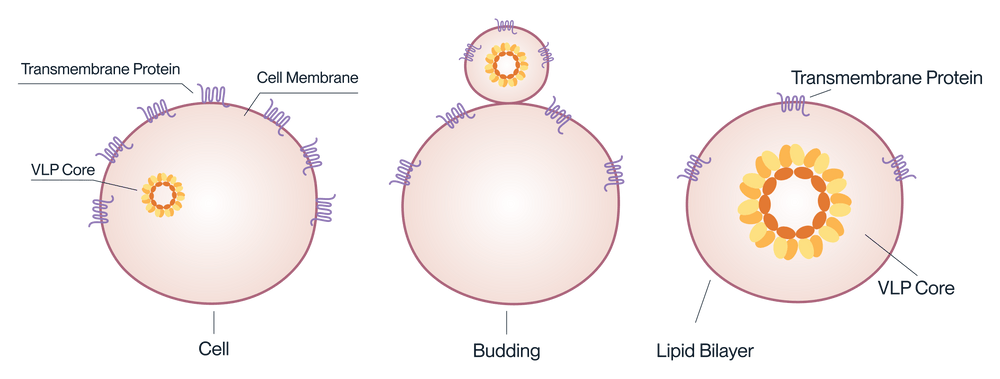
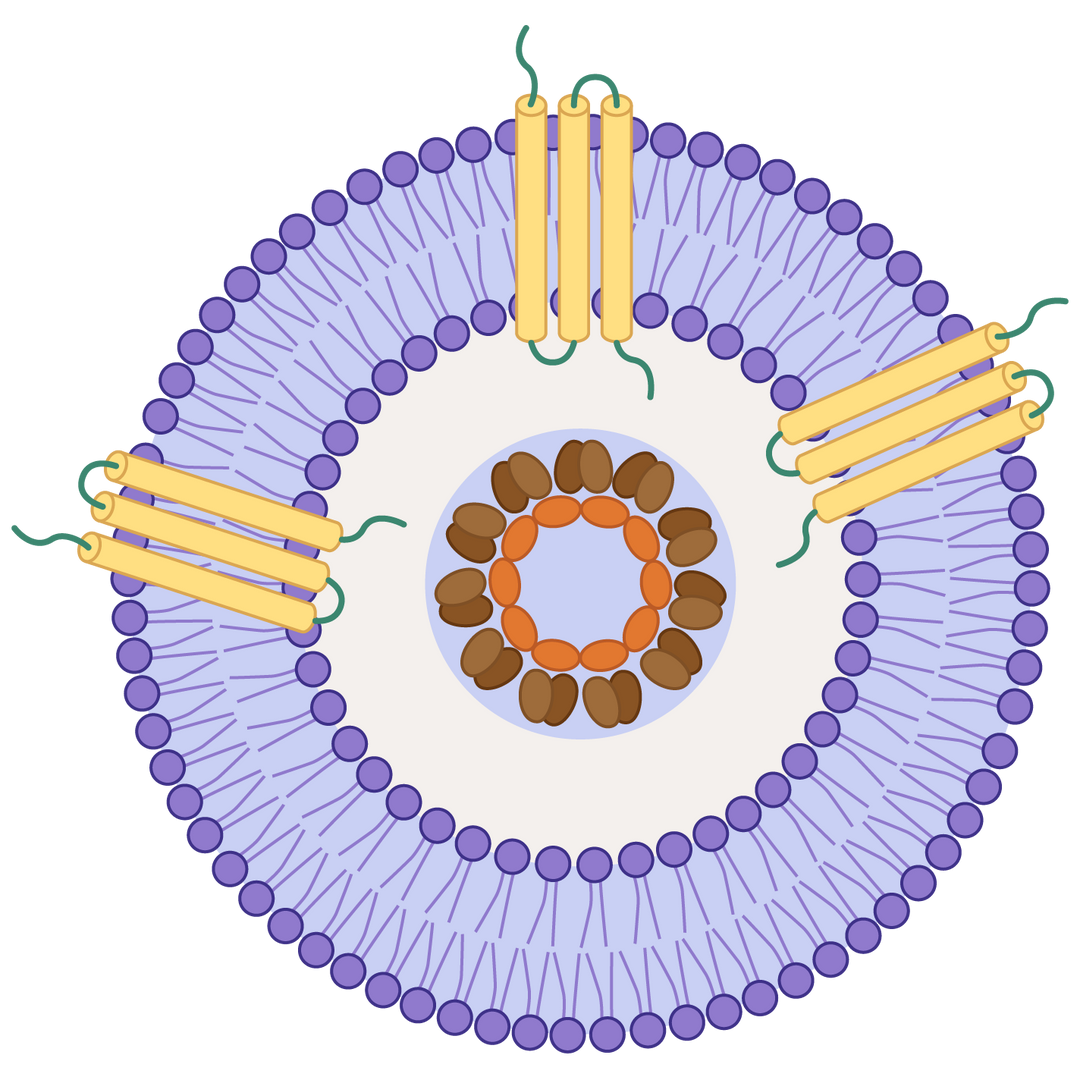
How the VLP displays transmembrane proteins.
Advantages of displaying membrane proteins on VLPs
Native-like Conformation: VLPs provide a lipid bilayer environment that helps transmembrane proteins maintain their correct folding, topology, and conformation, closely mimicking their native state on the cell membrane.
Enhanced Immunogenicity: The repetitive, multivalent display of antigens on VLPs significantly boosts immune responses compared to soluble or monomeric proteins, making them ideal for vaccine and antibody development.
Stabilization of Difficult Targets: Transmembrane proteins are often unstable or insoluble when isolated. VLPs offer structural support, increasing protein stability and solubility during purification and immunization.
Improved Antibody Generation: Presenting transmembrane proteins on VLPs enhances the likelihood of generating antibodies against conformational epitopes, which are often lost in linear peptide or denatured formats.
No Genetic Material = High Safety: VLPs are non-infectious because they lack viral genetic material, offering a safe platform for research and therapeutic development.
Product Features:
→ Mammalian cell expression system for natural folding and glycosylation
→ Strong Immunogenicity
→ Validated biological activity via ELISA and SPR
→ High batch-to-batch consistency
→ Site-specific biotinylation available
Applications:
→ Immunization
→ Antibody Screening
→ Analytical Assay Method Development and Testing
→ PK/PD studies
Product Validation
Claudin 18.2 is a tetraspanin protein family member of critical therapeutic potential for gastric and esophageal adenocarcinomas. Despite interest in drug development targeting Claudin 18.2, technical challenges in expressing high-quality Claudin 18.2 protein have significantly limited the progress of Claudin 18.2-targeted drug discovery and development. By leveraging virus-like particles, we have become the first company to successfully produce the commercially available, full-length human Claudin 18.2 protein in soluble format. Our consistent activity and purity testing results demonstrate the functional integrity and bioactivity of our VLP-displayed
protein platform.
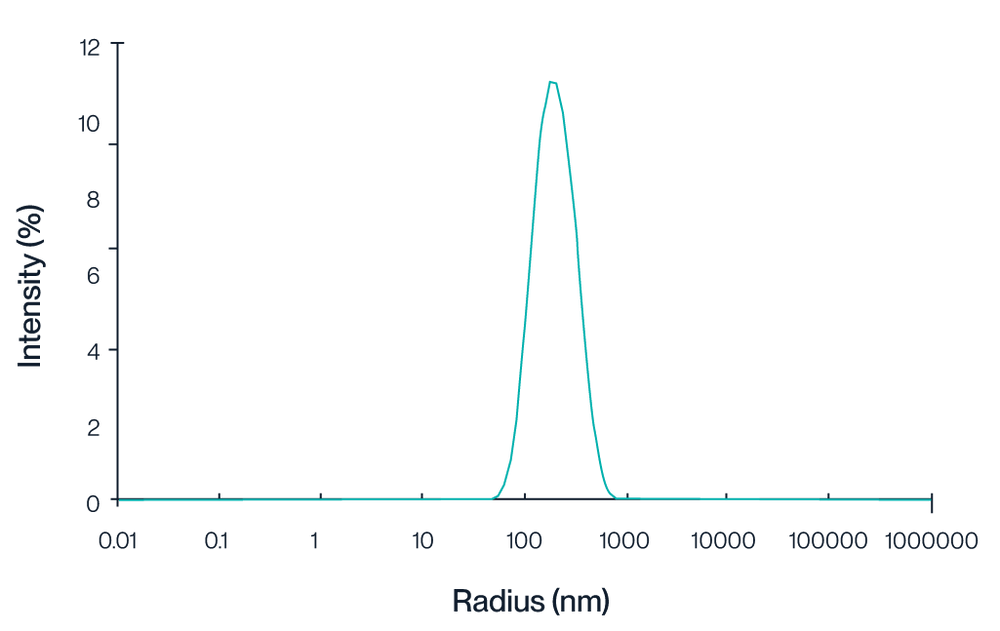
Figure 1. Intensity distribution of Claudin 18.2 VLPs measured by dynamic light scattering (DLS). The peak centered at approximately 150 nm indicates a homogeneous VLP particle size.
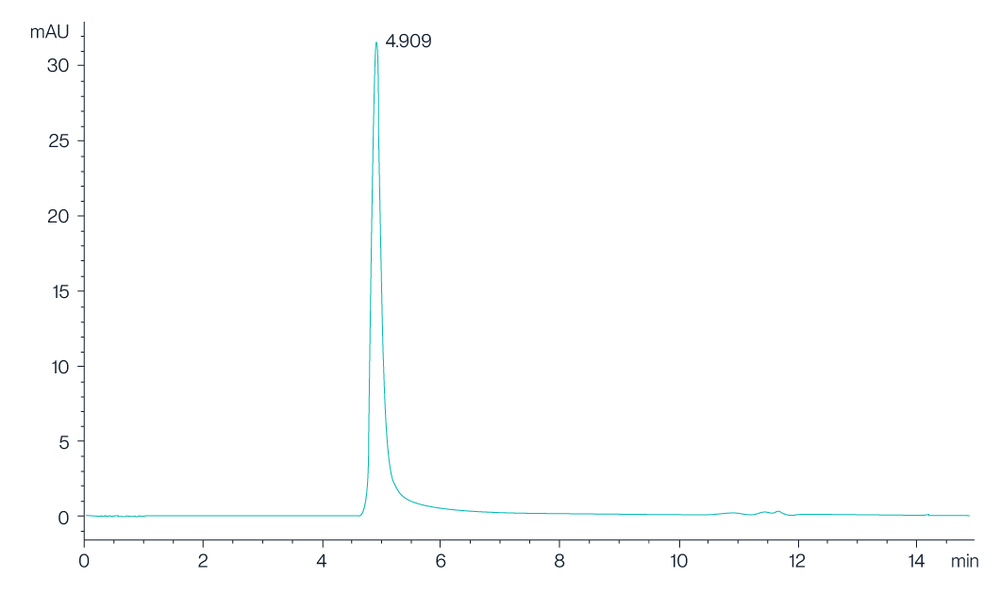
Figure 2. The chromatogram shows the high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) profile of Claudin 18.2 VLPs, with a prominent peak observed at 4.909 minutes, indicating the retention time of the Claudin 18.2 protein. The sharp and well-defined peak suggests a high purity and consistency of the VLP preparation.
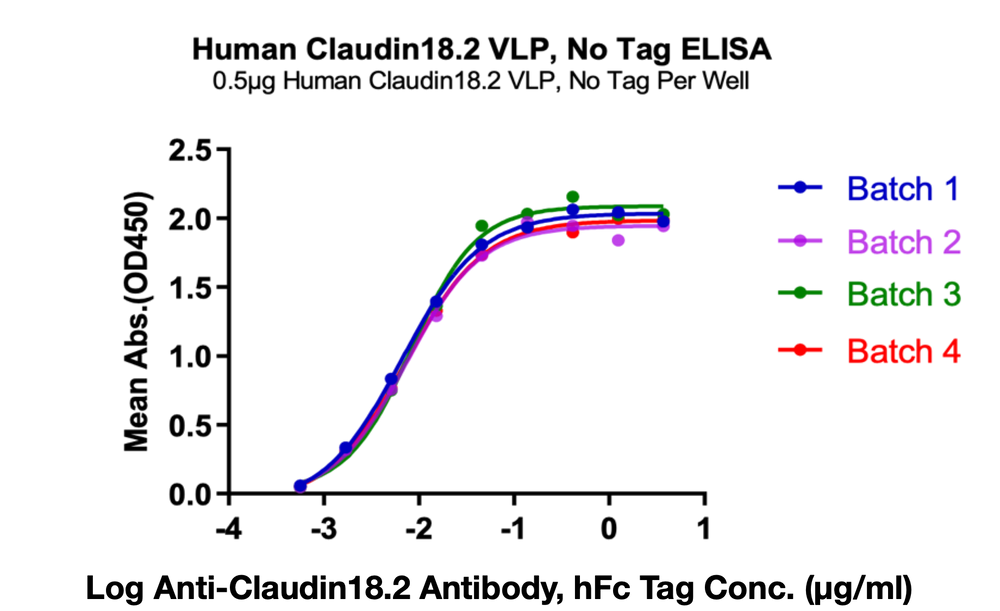
Figure 3. Immobilized Human Claudin 18.2 VLPs at 5ug/ml (100 ul/Well) on the plate. Dose response curve for Anti-Claudin 18.2 Antibody, hFc Tag with the EC50 of 6.6, 7.4, 8.3,7.3 ng/ml determined by ELISA.
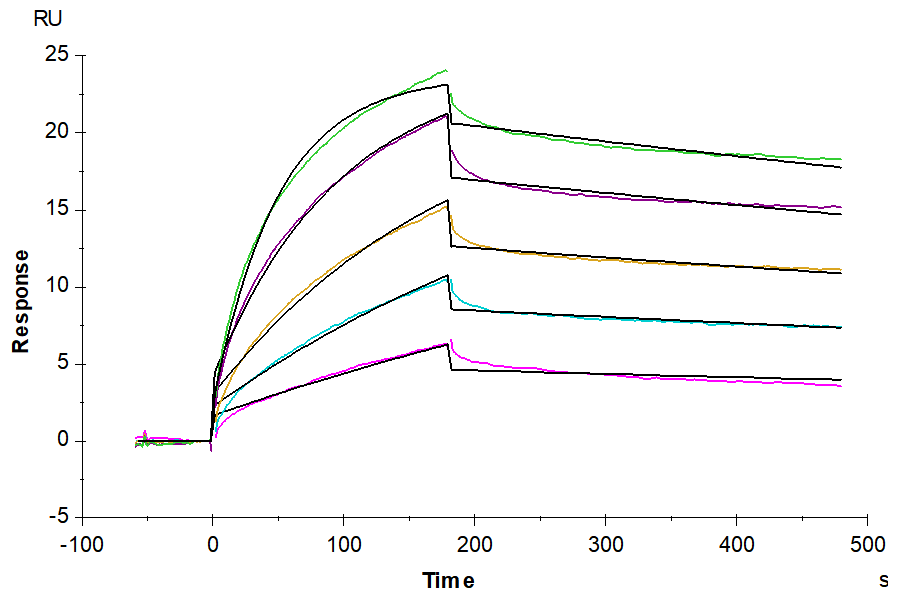
Figure 4. Biotinylated Claudin 18.2 VLPs captured on CM5 Chip via Streptavidin can bind Anti-Claudin18.2 Antibody with an affinity constant of 1.28 nM as determined in SPR assay (Biacore T200).
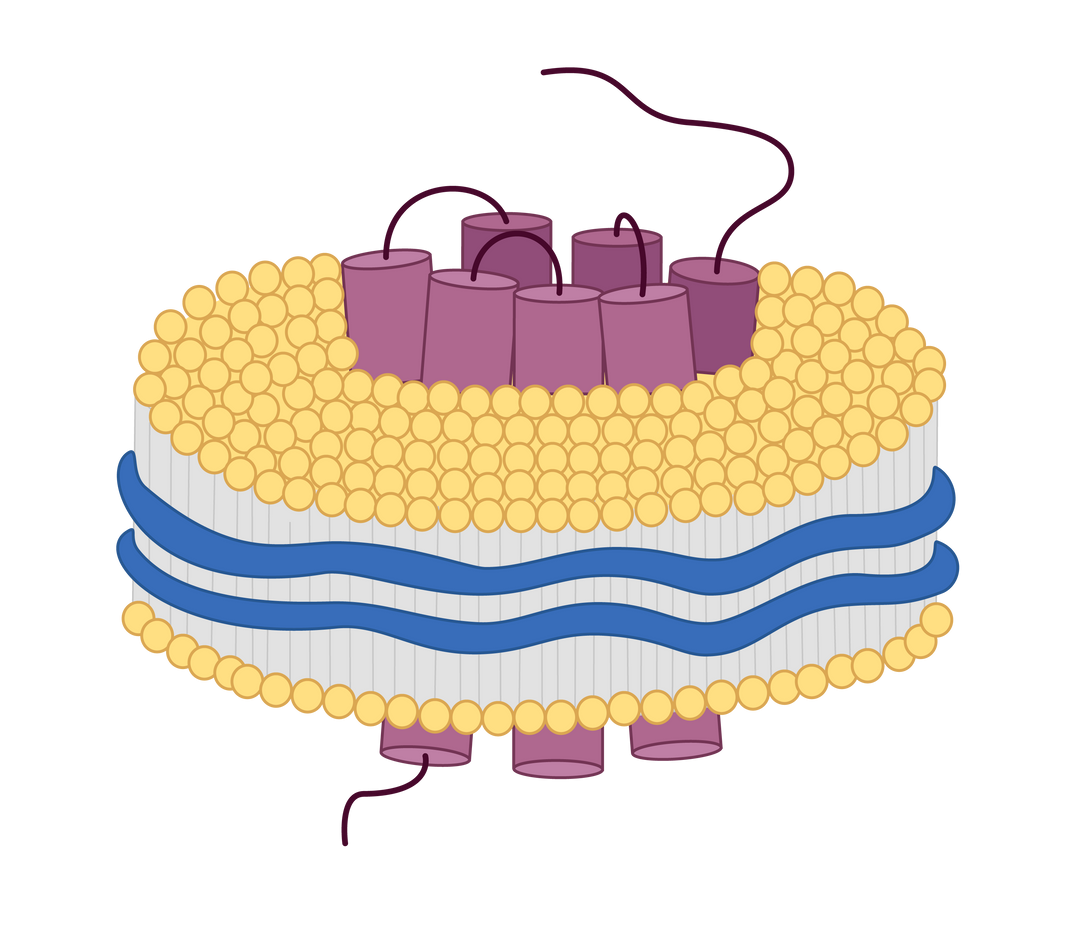
Nanodiscs are membrane-mimetic structures composed of a phospholipid bilayer and membrane scaffold proteins. They serve as important tools for stably displaying multi-pass transmembrane proteins with native conformation and protein activity. At KACTUS, we leverage a detergent-free production process to produce SMA-based nanodiscs as our catalog products to maximally maintain the native structure and conformation of the full-length, multi-pass transmembrane proteins in soluble format, allowing wide applications in drug screening, analytical assay development and testing.
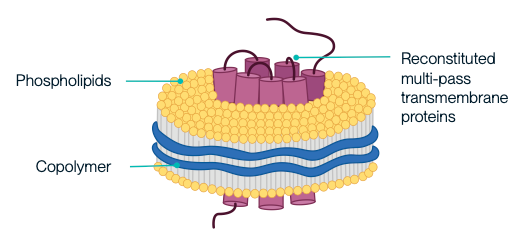
Structure & Expression
Full-length multi-pass transmembrane proteins are expressed in HEK293 cells. Copolymers interact with the membrane to form a disc-like structure around the target protein. The cellular phospholipids are retained, creating a stable nanodisc that mimics the natural membrane environment. This approach avoids the pitfalls of detergent extraction and streamlines the production process.
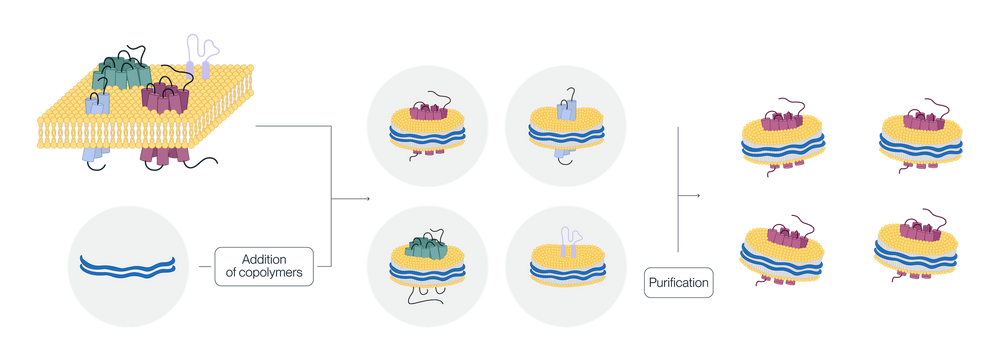
Advantages of displaying membrane proteins on SMA-Based Nanodisc
Detergent-Free Solubilization: SMA polymers solubilize membrane proteins directly from membranes without detergents, preserving delicate protein-lipid and protein-protein interactions.
Native Lipid Environment: Unlike synthetic nanodiscs (e.g., MSP-based), SMA nanodiscs contain endogenous lipids, which can be essential for structural integrity, function, and drug binding.
Better Protein Stability: Many membrane proteins remain more stable and active in SMA nanodiscs than in detergent micelles.
Broad Applicability: Effective for solubilizing a wide range of membrane proteins, including GPCRs, ion channels, and transporters.
Product Features
→ Mammalian cell expression system for natural folding and glycosylation
→ Detergent-free, natural phospholipid environment
→ Validated biological activity via ELISA and SPR
→ High batch-to-batch consistency
→ Site-specific biotinylation available
Applications
→ Antibody Panning
→ Antibody Screening
→ Analytical Assay Method Development and Testing
→ PK/PD studies
Introducing TCR-CD3 Nanodiscs: Eliminate Off-Target Antibodies
Traditional anti-CD3 antibody discovery often uses recombinant proteins, leading to an unproductive immune response against hidden, non-functional epitopes. This results in antibodies that bind strongly in vitro but fail to engage the native TCR/CD3 complex, causing extensive screening failure. KACTUS Nanodiscs deliver the complex in a native-like membrane environment, focusing the immune response on the functional epitopes and maximizing discovery efficiency.
Click here to learn more about these revolutionary nanodiscs.
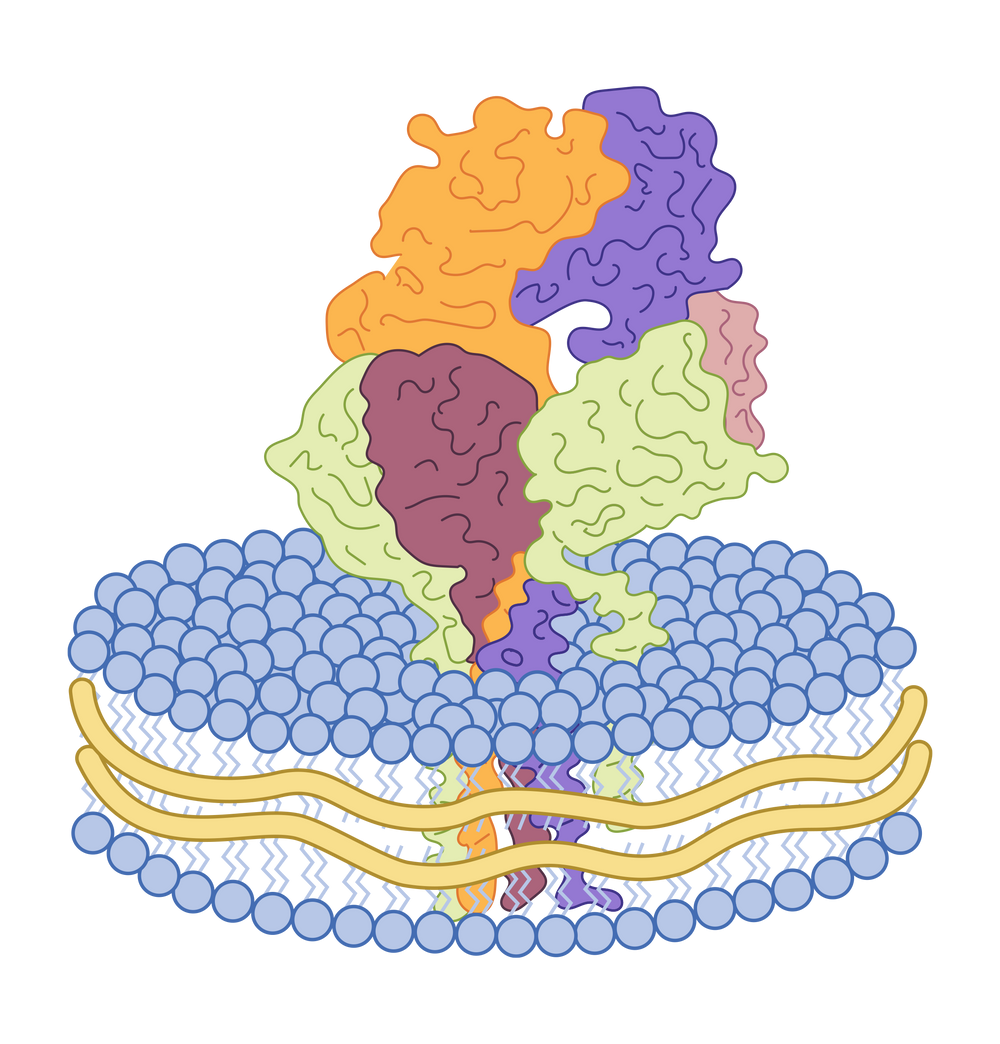
Product Validation
GPRC5D Nanodisc
GPRC5D is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) with 7-transmembrane domains. It is a popular target for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. This protein is being explored as a targeted in CAR-T cell therapy, and bispecific antibody drugs (with CD3 protein) for myeloma. To facilitate GPRC5D drug development, we have developed the full-length GPRC5D nanodisc with verified bioactivity through ELISA, BLI and SPR.
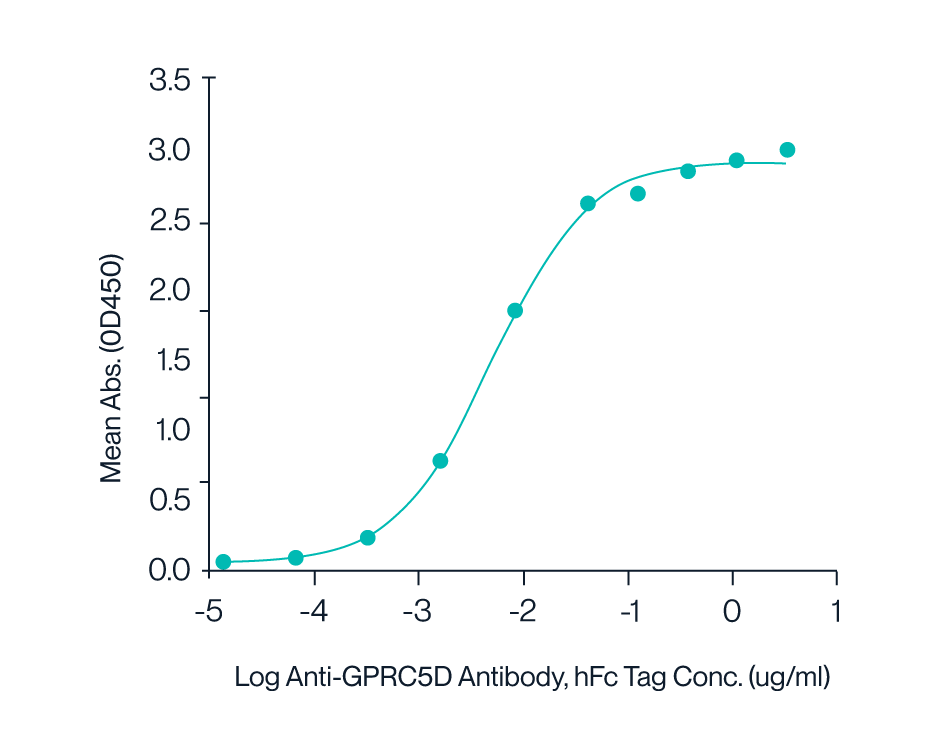
Figure 7. ELISA data demonstrates Human GPRC5D Nanodisc can bind to Anti-GPRC5D antibody with an EC50 of 4.9ng/mL.
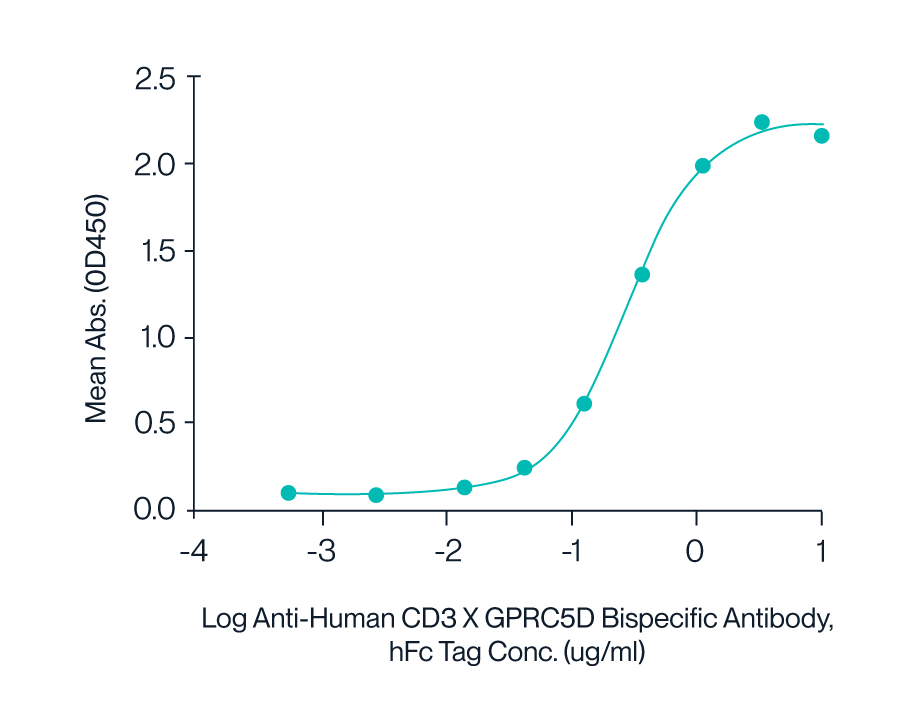
Figure 8. Human CD3E&CD3D was immobilized on the plate, followed by Anti-Human CD3×GPRC5D Bispecific Antibody binding, followed by Biotinylated Human GPRC5D Nanodisc. Results demonstrate quality performance in ELISA to of the nanodisc to Anti-Human CD3×GPRC5D bispecific antibody with an EC50 of 0.28 μg/mL.
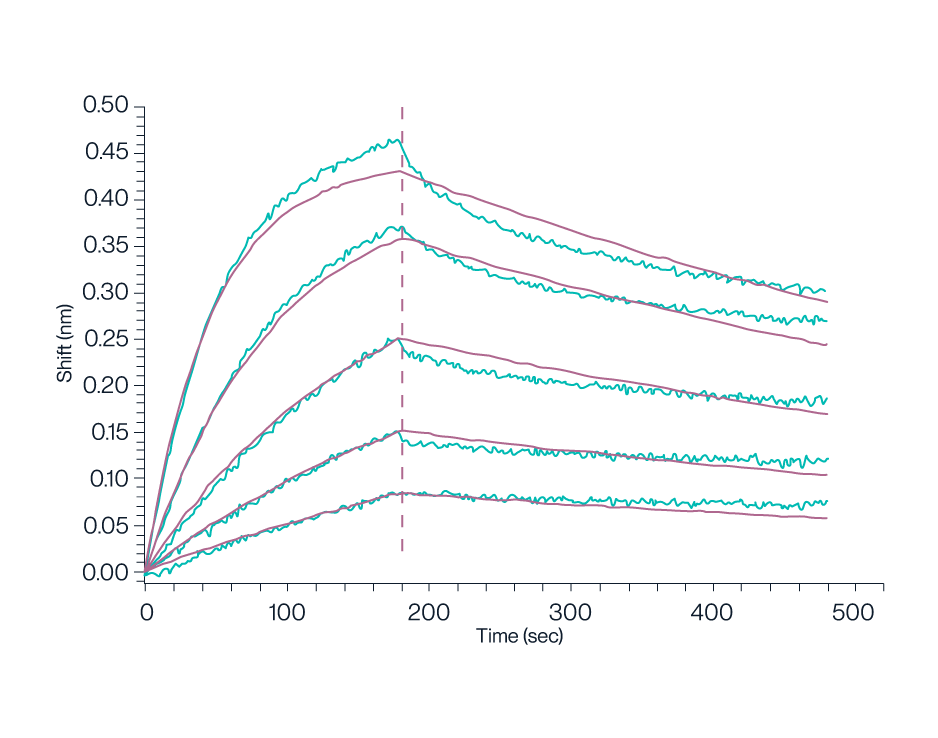
Figure 9. BLI data demonstrates Biotinylated Human GPRC5D Nanodisc can bind to Anti-GPRC5D Antibody with high affinity (KD=1.16nM).
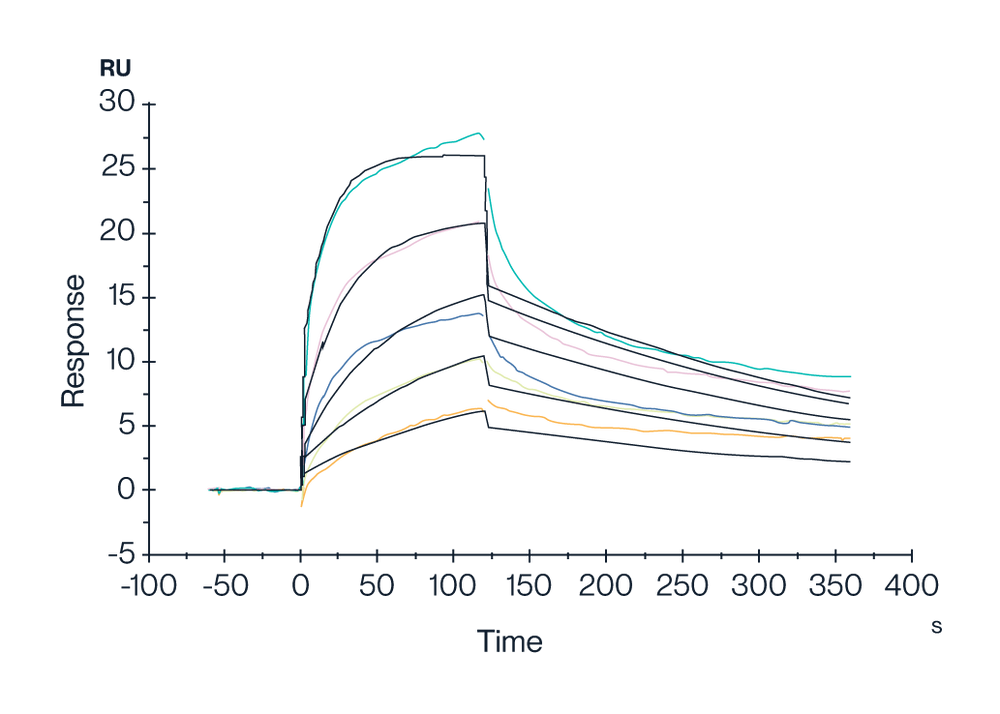
Figure 10. SPR data demonstrates Human GPRC5D Nanodisc can bind to Anti-GPRC5D Antibody with a high affinity (KD = 1.47nm).
Available Products
Multipass Transmembrane Proteins FAQs
VLPs (virus-like particles) and nanodiscs both serve as membrane-mimicking platforms, but they differ in structure and use. VLPs are self-assembled viral capsid proteins that allow multivalent antigen display, ideal for immunization and screening. Nanodiscs are disc-shaped lipid bilayers stabilized by copolymers, offering a more native-like environment for membrane proteins used in biophysical assays such as SPR, BLI, or ELISA.
We offer both liquid and lyophilized formats. Lyophilization improves long-term stability and flexibility in downstream use, particularly for screening and immunization. All lyophilized batches are tested post-reconstitution to ensure bioactivity and structural integrity.
Proteins are expressed in mammalian systems, allowing for native folding and extracellular domain exposure. For both formats, orientation is optimized to ensure correct presentation of extracellular loops or domains, which is critical for antibody discovery and binding assays. VLPs present the extracellular domain, keeping the intracellular component out of reach within the VLP. Nanodiscs allow access to both the extra- and intracellular components, allowing you to control the protein orientation on the chip via the protein tags.
While the exact number varies by protein size and capsid packing, each VLP is engineered for high-density display. We validate the presence and consistency of surface proteins through ELISA, flow cytometry, and biophysical characterization to ensure reproducibility across batches.
Our catalog includes His-tagged, biotinylated, and fluorescent-labeled formats. These enable compatibility with a variety of workflows including SPR, BLI, ELISA, and immunoprecipitation. Tagging details are listed per product in the catalog.
These products are validated for use in immunization, ELISA,phage display, SPR, BLI, and PK/PD modeling. The detergent-free nature of both platforms makes them ideal for preserving native protein structure and antigenicity.
All membrane protein products undergo batch-specific validation including size exclusion chromatography (SEC), dynamic light scattering (DLS), ELISA, and western blot (WB). This ensures batch-to-batch consistency, proper folding, and functional bioactivity. Additional QC such as SPR can be requested for a small fee.
Catalog products are shipped within 2–14 business days depending on stock availability. If a catalog item is in stock, we always use express overnight shipping. Custom orders typically require 6–8 weeks from project confirmation to delivery, including expression, purification, and validation.
Catalog items can be ordered online via credit card. For purchase orders or custom product requests, please contact us directly at orders@kactusbio.us or fill out the inquiry form on the product page.
Yes. Upon request, we provide a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) with validation data such as ELISA curves, BLI/SPR binding constants, and DLS size distribution. If needed, we can also schedule a consultation to discuss assay conditions or data interpretation.