Effective Serratia marcescens Nuclease for DNA & RNA Removal: MaxNuclease™
By Mallory Griffin
Nucleic acid removal is an essential step in biologics production workflows. Our MaxNuclease™ enzyme is a non-specific endonuclease from Serratia marcescens. This Benzonase® nuclease alternative offers a quality, cost-effective alternative for degrading both DNA and RNA in biological products. MaxNuclease™ provides comparable performance for nucleic acid digestion and is manufactured in our cGMP facility, making it suitable for commercial or preclinical biologics workflows.
Enzyme Characteristics
MaxNuclease™ is identified from Serratia marcescens and is a genetically engineered endonuclease expressed in E. coli (Escherichia coli). The endonuclease is manufactured in a cGMP facility with stringent quality release testing. MaxNuclease™ degrades all forms of nucleic acids including single- and double-stranded, linear and circular nucleic acids by hydrolyzing internal phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides to produce 5'-monophosphate oligonucleotides of 2-5 bases in length.
Quality Control Criteria
|
Assay |
Specification |
|
Activity (Dissolve herring sperm DNA) |
≥ 250 U/µL |
|
Purity (Bis-Tris) |
≥ 95% |
|
Purity (SEC-HPLC) |
≥ 99% |
|
Residual Protease |
Negative |
|
Residual Host Protein |
≤ 10 ppm |
|
Endotoxin |
≤ 0.01 EU/kU |
|
Sterility |
Negative |
|
Residual Heavy Metal |
≤ 10 ppm |
|
Mycoplasma |
Negative |
Product Performance Data
MaxNuclease™ exhibits comparable degradation activity to leading Serratia marcescens nuclease in host cell DNA removal and plasmid DNA removal.
Host Cell DNA Removal

Figure 1. Virus harvest solution was treated with 25U/mL and 50U/mL endonuclease at 37°C for 2 hours, respectively. Detection of Host Cell DNA (HCD) residue was analyzed. MaxNuclease™ has higher degradation activity versus Competitor B demonstrated by lower HCD residue for both 25U/mL and 50U/mL working concentrations.
Plasmid DNA Removal

Figure 2. Virus harvest solution was treated with 25U/mL and 50U/mL endonuclease at 37°C for 2 hours, respectively. Detection of plasmid DNA (pDNA) residue was analyzed. MaxNuclease™ has higher degradation activity versus Competitor B demonstrated by lower pDNA residue for both 25U/mL and 50U/mL working concentrations.
Degradation of PCR Product, Genomic DNA, and Plasmid DNA

Figure 3. MaxNuclease™ added to PCR product, genomic DNA, and plasmid DNA shows comparable degradation activity of nucleic acids to leading suppliers.
Applications
-
Biologics Workflows: Remove nucleic acids in industrial biological products such as vaccines, polysaccharides, and recombinant proteins, to meet regulatory requirements and improve product efficacy.
-
Viscosity Reduction: Reduce the viscosity of cell lysates and cell clumping, increasing protein yield, improving separation effect, making it easy to filter (especially ultrafiltration), and facilitate downstream chromatographic purification workflows.
-
Viral Vector Production: Remove unwanted nucleic acids in gene therapy vector preparations, such as AAV and lentiviral vectors, to avoid aggregation in cell products and improve purification efficiency.
-
Viral Vaccine Production: Reduce host-derived nucleic acids and plasmid DNA during vaccine manufacturing, decreasing viscosity and preventing aggregate formation, to improve downstream processing.
-
Sample Preparation: Improve resolution and recovery in biochemical analysis such as ELISA, chromatography, two-phase electrophoresis, and footprinting analysis, by degrading nucleic acids in samples.
Operating Conditions
MaxNuclease™ has the following optimal and effective reaction conditions:
|
Condition |
Optimal* |
Effective** |
|
Mg2+ |
1-2mM |
1-10mM |
|
Na+, K+ |
0-100mM |
0-300mM |
|
pH |
8-10 |
4-10 |
|
Temperature |
37℃ |
0-50℃ |
|
PO43- |
0-10mM |
0-80mM |
*The condition under which MaxNuclease™ retains >90% of its activity
**The condition under which MaxNuclease™ retains >15% of its activity
Effect of Temperature

Figure 4. Effect of temperature on MaxNuclease™ activity. The relative activity rises with increasing temperature. The optimum temperature is 37°C-42°C.
Effect of pH

Figure 5. Effect of pH on MaxNuclease™ endonuclease activity. The optimum pH is between 8 and 10.
Stability Testing

Figure 6. Stability of MaxNuclease™ at 37°C and 25°C. The relative activity is stable when stored at 37°C and 25°C for up to 7 days.

Figure 7. Freeze-thaw stability of MaxNuclease™. The relative activity is stable when MaxNuclease™ is freeze/thawed between -80°C to 4°C and -20°C to 25°C up to 12 times.
MaxNuclease™ ELISA Kit
After nucleic acid removal using MaxNuclease™, the residual enzyme in the product or sample must be evaluated. For residual MaxNuclease™ detection, KACTUS has developed a highly sensitive and specific sandwich ELISA quantification kit, with a sensitivity of up to 23 pg/mL.
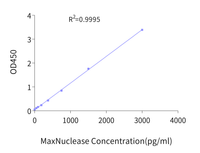
Example Standard Curve

Figure 7. Example 8-point standard curve for MaxNuclease™ ELISA kit to quantify residual MaxNuclease™ enzyme.
Affordable Endonuclease for Biologics Production Small and Large Scale
MaxNuclease™ is an active and reliable alternative to Benzonase® nuclease for nucleic acid removal in various biologics manufacturing processes. Its high efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and GMP-grade production make it a valuable nuclease for viral vaccine, viral vector, and recombinant protein production workflows. MaxNuclease™ is suitable for small and large-scale production and is available in a consistent, long-term supply. To learn more about MaxNuclease™, please contact us at support@kactusbio.us.
Request a quote or test sample →
Products
Additional Resources
Benzonase® is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA. MaxNuclease™ is a product of KactusBio Inc.